Google is the most popular search engine in the world, but did you know that you can use it to find more than just web pages? You can also use Google advanced search operators to refine your search queries and get more specific results.

In this article, I will show you how to use these operators and some examples of how they can help you with your online research.
What are Google advanced search operators?
Google advanced search operators are special commands that you can add to your search query to modify how Google interprets and returns your results. They can help you narrow down your search, filter out irrelevant results, or find specific types of information.
For example, if you want to find web pages that contain the exact phrase "how to write a blog post", you can use quotation marks around your query like this:
"how to write a blog post"
This will tell Google to only show you results that match the exact words and order of your phrase. This can be useful if you are looking for a specific piece of information or a quote.
Another example is if you want to find web pages that are related to a certain topic, but not necessarily contain your query words. You can use the tilde operator (~) before your query like this:
~blogging
This will tell Google to show you results that are synonyms or related terms of your query. This can be useful if you want to explore different aspects or variations of a topic.
There are many more Google advanced search operators that you can use, and I will explain them in detail in the following sections.

How to use Google advanced search operators
To use Google advanced search operators, you need to follow some rules and syntax. Here are some general tips to keep in mind:
-
Use a colon (:) after the operator and no space before your query. For
example,
site:example.comnotsite: example.com. -
Use quotation marks (") around your query if it contains more than one word
or an exact phrase. For example,
"content marketing"notcontent marketing. -
Use a minus sign (-) before an operator or a query term to exclude it from
your results. For example,
-site:example.comor-"content marketing". -
Use a vertical bar (|) or OR between query terms to include either one of
them in your results. For example,
blogging|content marketingorblogging OR content marketing. -
Use parentheses () around your query terms to group them together and apply
operators to them. For example,
(blogging|content marketing) -site:example.com. -
Use an asterisk (*) as a wildcard to replace any word or phrase in your
query. For example,
"how to * a blog post".
List of Google advanced search operators
Here is a list of the most common and useful Google advanced search operators that you can use for different purposes. I will also provide some examples of how to use them and what results they will return.
site:
The site operator allows you to limit your search to a specific website or domain. You can use it to find information from a certain source or check how many pages of a website are indexed by Google.
For example, if you want to find all the pages from example.com that mention blogging, you can use this query:
site:example.com blogging
This will show you results like this:
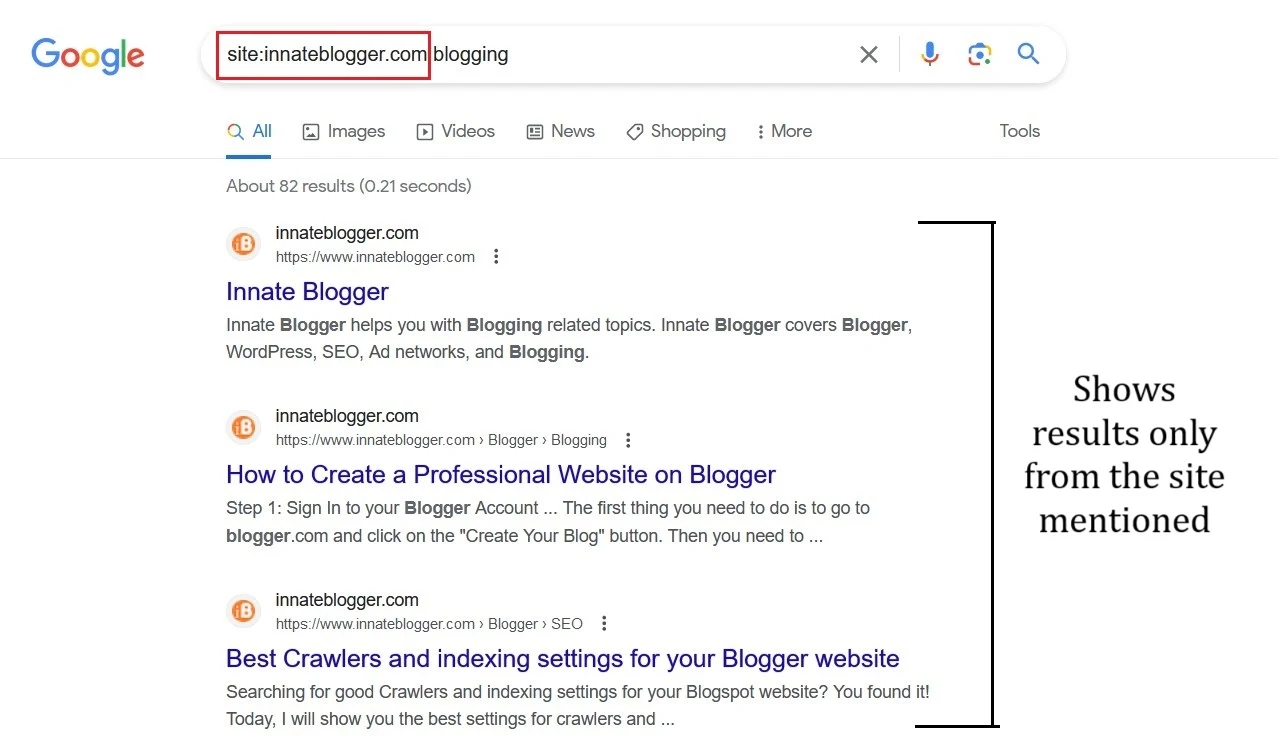
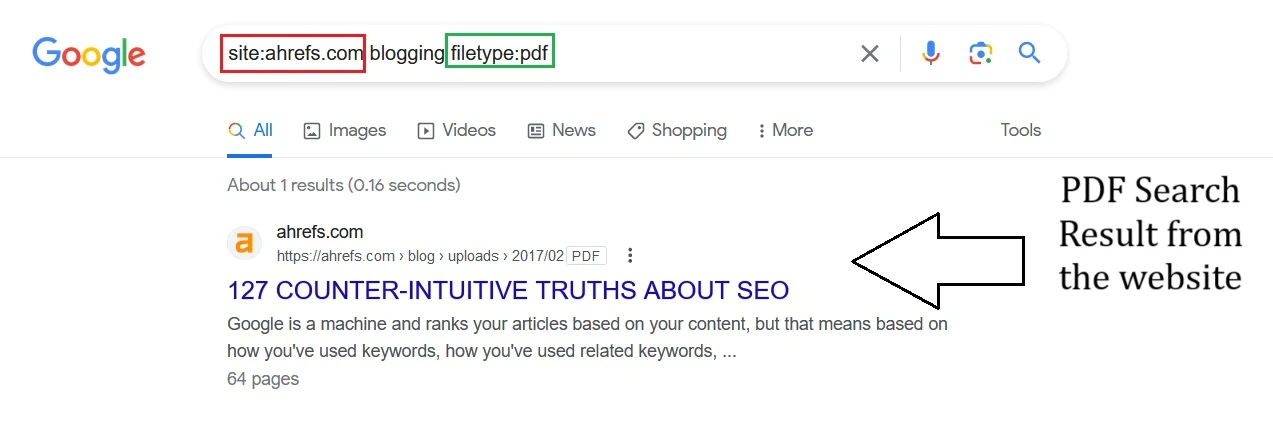
You can also use the site operator with other operators or query terms to refine your search further. For example, if you want to find all the PDF files from example.com that mention blogging, you can use this query:
site:example.com blogging filetype:pdf
This will show you results like this:
intitle:
The intitle operator allows you to find web pages that contain your query term in their title tag. The title tag is the text that appears at the top of your browser tab and in the search results snippet. It is usually an indicator of what the page is about.
For example, if you want to find web pages that have the word blogging in their title, you can use this query:
intitle:blogging
You can also use the intitle operator with other operators or query terms to refine your search further. For example, if you want to find web pages that have the word blogging in their title and the word content in their URL, you can use this query:
intitle:blogging inurl:content
inurl:
The inurl operator allows you to find web pages that contain your query term in their URL. The URL is the address of the web page that appears in your browser bar and in the search results snippet. It is usually composed of the domain name and the path of the page.
For example, if you want to find web pages that have the word blogging in their URL, you can use this query:
inurl:blogging
You can also use the inurl operator with other operators or query terms to refine your search further. For example, if you want to find web pages that have the word blogging in their URL and the word tips in their title, you can use this query:
inurl:blogging intitle:tips
filetype:
The filetype operator allows you to find web pages that are of a specific file type. You can use it to find documents, images, videos, or any other file format that you are looking for.
For example, if you want to find PDF files that mention blogging, you can use this query:
derivative formula mathematics filetype:pdf
This will show you results like this:

You can also use the filetype operator with other operators or query terms to refine your search further. For example, if you want to find PDF files from example.com that mention blogging, you can use this query:
site:example.com derivative formula mathematics filetype:pdf
related:
The related operator allows you to find web pages that are similar or related to a specific URL. You can use it to discover new websites or sources of information that are relevant to your topic.
For example, if you want to find web pages that are similar or related to example.com, you can use this query:
related:example.com
You can also use the related operator with other operators or query terms to refine your search further. For example, if you want to find web pages that are similar or related to example.com and mention blogging, you can use this query:
related:example.com blogging
cache:
The cache operator allows you to view a cached version of a web page. A cached version is a snapshot of how the page looked when Google last crawled it. You can use it to see how a page has changed over time or to access a page that is no longer available.
For example, if you want to view a cached version of example.com, you can use this query:
cache:example.com
You can also use the cache operator with other operators or query terms to refine your search further. For example, if you want to view a cached version of example.com and highlight the word blogging, you can use this query:
cache:example.com blogging
How to use Google advanced search operators for SEO
Google advanced search operators can be very useful for SEO (search engine optimization) purposes. You can use them to perform various tasks such as:
- Keyword research: You can use Google advanced search operators to find relevant keywords for your niche or topic. For example, you can use the tilde (~) operator to find synonyms or related terms of your main keyword. You can also use the asterisk (*) operator to find variations or modifiers of your keyword.
- Competitor analysis: You can use Google advanced search operators to spy on your competitors and see what they are ranking for. For example, you can use the site operator to see how many pages of their website are indexed by Google. You can also use the intitle or inurl operators to see what keywords they are targeting in their title tags or URLs.
- Link building: You can use Google advanced search operators to find link building opportunities for your website. For example, you can use the related operator to find websites that are similar or related to yours. You can also use the filetype operator to find resource pages or directories that accept submissions of your file type.
- Content creation: You can use Google advanced search operators to find content ideas for your website. For example, you can use the quotation marks (") operator to find popular phrases or questions that people are searching for. You can also use the cache operator to see how a web page has changed over time and get inspiration from it.
Conclusion
Google advanced search operators are powerful tools that can help you find more relevant and specific results for your online research. They can also help you with various SEO tasks such as keyword research, competitor analysis, link building, and content creation.
By learning how to use them effectively, you can improve your online skills and get more out of Google.
